News | Press Releases
For Immediate Release Contact marketingcommunications@us.medical.canon
November 18, 2024
Verification of Noninvasive Evaluation Methods for Hepatic Steatosis, Inflammation, and Fibrosis Using the “Liver Package” for Aplio i-series Diagnostic Ultrasound Systems
Otawara, Tochigi, Japan, November 14, 2024 — Canon Medical Systems Corporation (hereinafter “Canon Medical”; President and CEO: Toshio Takiguchi; headquarters: Otawara, Tochigi, Japan) has been supporting research to verify noninvasive evaluation methods for liver disease using a set of applications “Liver Package” for Aplio i-series diagnostic ultrasound systems. In an international multicenter study known as the iLEAD Study (innovative Liver Elasticity, Attenuation, and Dispersion ultrasound study), it was found that the diagnostic data obtained using Attenuation Imaging (ATI), Shear Wave Dispersion (SWD), and Shear Wave Elastography (SWE), which are applications that support “Liver Package,” show good correlations with the degree of hepatic steatosis, inflammation, and fibrosis. A paper reporting the clinical evidence and results obtained in this study has been published in the leading academic journal Radiology.
Another multicenter study known as the ATiMIC Study (Attenuation image Multi-Institution Center
study) has also verified the accuracy of ATI for the diagnosis of hepatic steatosis. The results of this study
are scheduled to be presented at The 75th Liver Meeting of the American Association for the Study of
Liver Diseases (AASLD) to be held in San Diego starting on November 15, 2024.
In recent years, the number of cases of hepatic steatosis as a cause of chronic liver disease has been
rapidly increasing, leading healthcare professionals to propose the establishment of a new disease entity
called metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD), which is not associated with
alcohol consumption or other liver diseases. The liver is considered a “silent organ” because the early
stages of liver diseases are asymptomatic, but these diseases can progress to steatohepatitis, liver
cirrhosis, and liver cancer. Early detection is therefore essential. However, in order to evaluate liver
diseases and monitor the effects of treatment, it is often necessary to perform liver biopsy, an invasive
procedure in which pieces of liver tissue are sampled and examined under a microscope. Liver biopsy
places a significant burden on the patient, so there is great interest in developing noninvasive evaluation
methods that can easily be employed in the clinical setting. It is expected that the research described
here will lead to the introduction of noninvasive liver disease evaluation methods for routine medical
use in the near future.
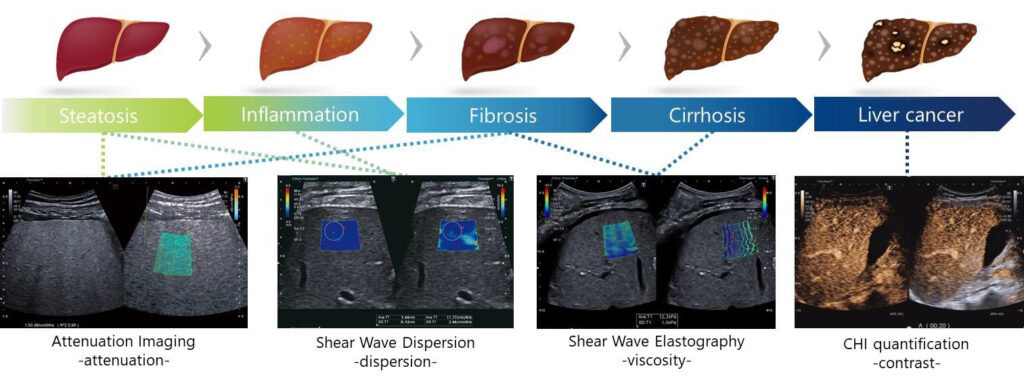
Features of the Liver Package and results obtained in the iLEAD Study
- Attenuation Imaging (ATI)
This application is for measuring frequency-dependent attenuation coefficient in liver tissue
based on the characteristic weakening of ultrasound signals as they penetrate deep into tissues.
In the iLEAD Study, it was found that the attenuation coefficient (AC) obtained by ATI showed
good correlation with the degree of hepatic steatosis. - Shear Wave Dispersion (SWD)
This application is for analyzing the dispersion in the velocities of shear waves of different
frequencies as they propagate within tissues. It measures dispersion of shear wave propagation
and visualizes tissue viscosity. In the iLEAD Study, it was found that the dispersion slope (DS)
obtained by SWD showed good correlation with the degree of hepatic inflammation. - Shear Wave Elastography (SWE)
This application shows tissue stiffness by measuring shear wave velocity and provides a dynamic
display with 4 smart maps. In the iLEAD Study, it was found that the shear wave speed obtained
by SWE showed good correlation with the degree of hepatic fibrosis.
Measurement tools suitable for evaluating various stages of liver disease
The iLEAD Study
This multicenter study was conducted by Professor Emeritus Fuminori Moriyasu of Tokyo Medical
University and Associate Professor Katsutoshi Sugimoto of the Department of Gastroenterology
and Hepatology of Tokyo Medical University, working in cooperation with other researchers. In this
study, the ultrasound imaging markers DS, AC, and SWS were measured in patients with metabolic
dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD) and metabolic dysfunction-associated
steatohepatitis (MASH) as diagnosed by liver biopsy. The correlations between each imaging
marker and the pathological findings of inflammation, steatosis, and fibrosis were then analyzed.
This research was conducted as an international multicenter study involving institutions in Japan,
other Asian countries, the United States, and Europe. The results of the study were published in the
international academic journal Radiology on August 20, 2024. The study verified that SWD, ATI, and
SWE are useful for evaluating hepatic inflammation, steatosis, and fibrosis. It is therefore anticipated
that these methods will be employed for the noninvasive evaluation of liver diseases in routine
clinical practice.
The ATiMIC Study
With Professor Hiroko Iijima of the Department of Hepatobiliary and Pancreatic Disease of Hyogo
College of Medicine serving as the research supervisor, this multicenter study is being conducted at 11
institutions in Japan. In this study, the diagnostic information obtained using ATI is compared against
the results of liver biopsy and the proton density fat fraction (PDFF, which measures the hepatic
fat/water ratio in MR images) to verify the accuracy of ATI for the diagnosis of hepatic steatosis. It is
difficult to diagnose hepatic steatosis using conventional B-mode imaging when the amount of fat in
the liver is small. The use of ATI in such cases is expected to provide objective data concerning disease
progression, which may make it possible to diagnose MASLD and MASH in the early stages. The results
of this research are scheduled to be presented at The 75th Liver Meeting of the American Association
for the Study of Liver Diseases (AASLD) to be held in San Diego starting on November 15, 2024.
Based on the evidence obtained in these studies, Canon Medical Systems will further develop and
promote our applications to support the early detection and diagnosis of liver diseases.
About Canon Medical Systems Corporation
Canon Medical offers a full range of diagnostic medical imaging solutions including CT, X-Ray,
Ultrasound, Vascular and MR, as well as a full suite of Healthcare IT solutions, across the globe. In
line with our continued Made for Life philosophy, patients are at the heart of everything we do. Our
mission is to provide medical professionals with solutions that support their efforts in contributing
to the health and wellbeing of patients worldwide. Our goal is to deliver optimum health
opportunities for patients through uncompromised performance, comfort and safety features.
At Canon Medical, we work hand in hand with our partners – our medical, academic and research
community. We build relationships based on transparency, trust and respect. Together as one, we
strive to create industry-leading solutions that deliver an enriched quality of life. For more
information, visit the Canon Medical website: https://global.medical.canon